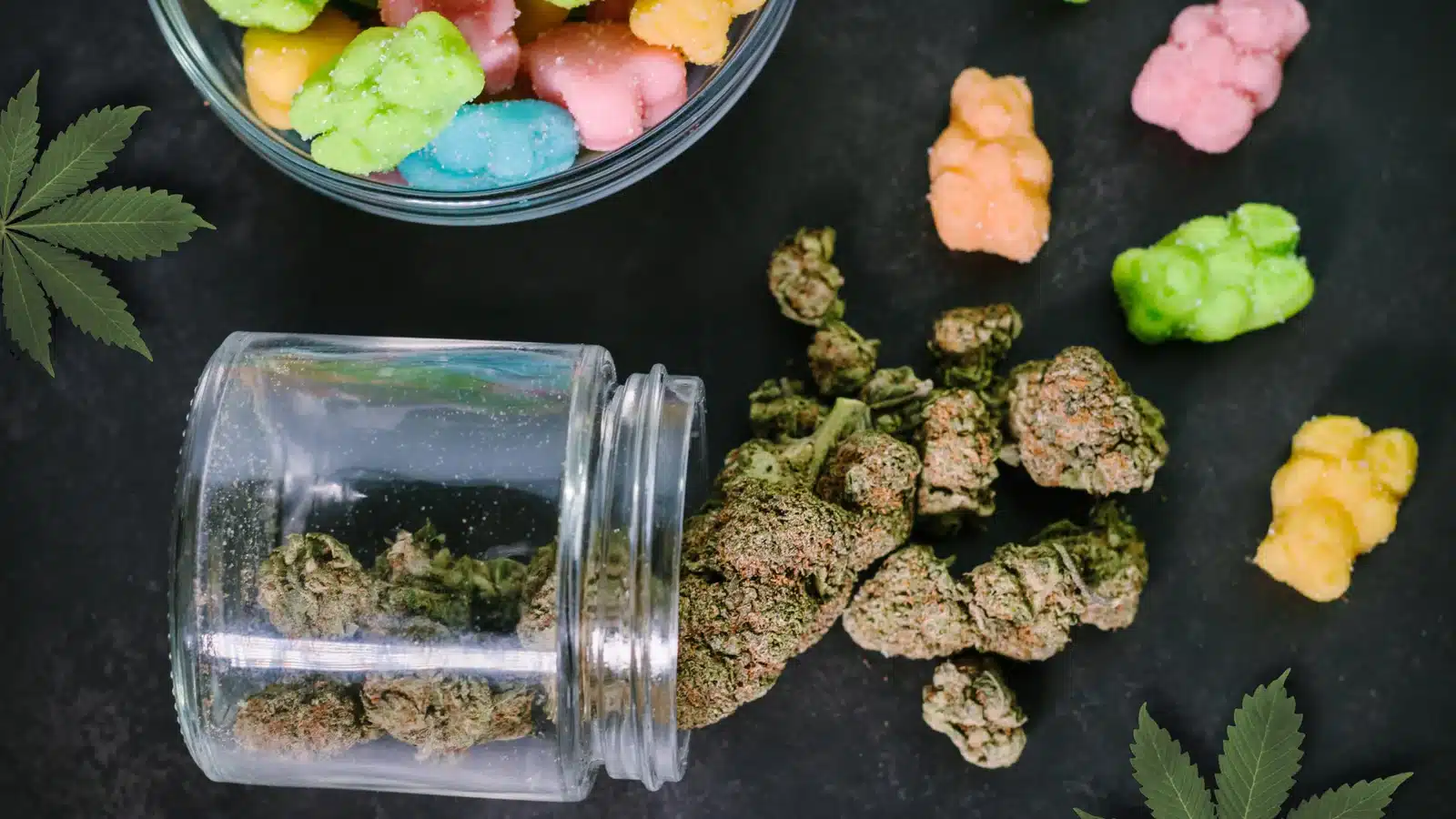
There is a growing interest in cannabis-infused edibles as people look for alternatives to traditional cannabis consumption methods. One exciting component that has gained attention is THCA, which is found in raw cannabis and acts as a non-psychoactive form of THC.
When THCA is heated or aged, it transforms into THC, unlocking therapeutic properties without causing intoxication. This opens the door to exploring the role of THCA in edibles, examining its chemistry, potential health benefits, and the changing landscape of cannabis-infused cuisine.
So, the question is: Can THCA be used in edibles? Yes, indeed. Although THCA does not have psychoactive effects in its raw state, its conversion to THC when exposed to heat or time offers the potential for infused products with therapeutic benefits without the usual intoxicating effect associated with THC.
Hence, understand THCA’s potential in edibles. Whether you’re curious about new ways to use cannabis or just love trying tasty treats from one of the best Delta 8 brands, this article will give you the scoop on THCA in edibles.
Table of Contents
Understanding THCA
THCA is the acidic precursor to THC, the primary psychoactive compound in cannabis. When cannabis is in its raw form, THCA is present in higher concentrations. THCA is converted to THC through a process called decarboxylation, which occurs when cannabis is exposed to heat. This transformation is crucial in understanding the differences between consuming raw cannabis versus heated or processed forms.
Chemical Structure and Properties
THCA has a similar chemical structure to THC, with the critical difference being the presence of a carboxylic acid group. This group makes THCA non-psychoactive, as it does not bind well to cannabinoid receptors in the brain responsible for the psychoactive effects. Decarboxylation removes this group, converting THCA to THC, which can then interact with these receptors.
Brief On THCA In Edibles
The use of edibles is gaining popularity among those seeking the therapeutic benefits of cannabis without the high. To incorporate THCA into edibles, avoiding decarboxylation during preparation and cooking is essential.
Preparation and Preservation
To maintain the integrity of THCA gummies, edibles must be prepared at low temperatures. This means using raw cannabis or extracts that have not been exposed to heat. Smoothies, juices, and cold-infused dishes are examples of edibles that can contain THCA. Additionally, storing these edibles at low temperatures helps preserve the THCA content.
Practical Tips For Incorporating THCA Into Edibles
For those interested in experimenting with THCA edibles, here are some practical tips:
- Choose Raw or Live Cannabis: Use raw cannabis flowers or fresh leaves, which contain higher levels of THCA. Avoid dried or cured cannabis, as these have lower THCA content.
- Avoid Heat: Avoid using high temperatures when preparing edibles. Cold infusion methods are ideal, such as making cold-pressed juices or smoothies.
- Proper Storage: Store THCA edibles in the refrigerator or freezer to maintain their potency. Exposure to light, heat, and air can degrade THCA over time.
- Experiment with Recipes: Incorporate THCA into a variety of dishes, such as salads, cold soups, and raw desserts. This allows for creative and enjoyable ways to consume THCA without losing its benefits.
- Consult a Professional: Speak with a healthcare provider or a cannabis specialist to understand the appropriate dosing and potential interactions with other medications.
Some Potential Health Benefits Of THCA
While research is still ongoing, THCA has shown promise in various therapeutic applications:
Anti-inflammatory Properties
THCA is believed to possess significant anti-inflammatory properties. Studies suggest that it may help reduce inflammation, which is beneficial for conditions like arthritis and other inflammatory diseases. The anti-inflammatory effects of THCA are due to its ability to inhibit the production of pro-inflammatory compounds.
Neuroprotective Effects
Research indicates that THCA may have neuroprotective properties, potentially offering protection against neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s. These effects are believed to stem from its ability to reduce oxidative stress and inflammation in the brain.
Anti-emetic and Anti-proliferative Effects
THCA has also been studied for its anti-emetic properties, which could be helpful for patients undergoing chemotherapy. Additionally, preliminary studies suggest that THCA may have anti-proliferative effects on cancer cells, although more research is needed to confirm these findings.
Differences Between THCA And THC In Edibles
When comparing edibles made with THCA versus those made with THC, the primary difference lies in the psychoactive effects. THCA edibles do not produce the high associated with THC, making them a suitable option for individuals seeking therapeutic benefits without the psychoactive experience.
Dosing and Administration
Dosing for THCA edibles can differ from THC edibles due to the lack of psychoactive effects. This allows for potentially higher doses of THCA without the risk of intoxication. However, starting with small doses and gradually increasing is essential to monitor the body’s response and avoid any adverse effects.
Legal Considerations
The legal status of THCA varies by region. In some areas, THCA is treated similarly to THC and is subject to the same regulations. In other places, THCA may be legal if it is not decarboxylated. Consumers and manufacturers must be aware of local laws regarding the use and sale of THCA products.
Research And Future Directions Of THCA
Our understanding of THCA remains in its early phases, requiring additional research to grasp its potential benefits and risks comprehensively. Future studies will likely delve into its mechanisms of action, optimal dosages, and long-term effects. As the legal landscape surrounding cannabis undergoes transformation, more opportunities for research and development of THCA-based products are expected to emerge.
Exploring THCA’s mechanisms of action is crucial for elucidating how it interacts with the body and potentially alleviates various conditions. Determining the most effective dosages will ensure its safe and optimal use for therapeutic purposes. Moreover, investigating the long-term effects of THCA consumption will provide valuable insights into its safety profile and sustainability as a treatment option.
With shifting attitudes towards cannabis and its derivatives, there is a growing acceptance of exploring alternative cannabinoids like THCA for medicinal purposes. This evolving legal framework fosters scientific exploration and encourages innovation in developing new THCA-based products tailored to address specific health needs. As research continues to unfold, THCA holds promise as a potential therapeutic agent, contributing to the expanding repertoire of cannabis-derived treatments available to patients.
Final Take: Everything You Need To Know About THCA Edibles
THCA presents a promising avenue for those interested in the therapeutic benefits of cannabis without the psychoactive effects.
Its potential anti-inflammatory, neuroprotective, and anti-emetic properties make it an attractive option for various health conditions.
However, preparing THCA edibles requires careful attention to avoid decarboxylation and preserve the compound’s integrity.
As research progresses and the legal environment changes, THCA may become a more prominent component of the cannabis wellness industry.